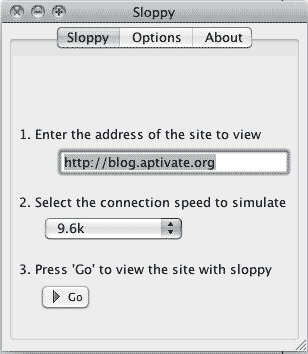
In today’s hyper-connected world, the expectation of seamless app performance is pervasive. However, not every region possesses robust internet infrastructure. Simulating low bandwidths is an essential practice for app developers aiming to ensure their applications perform optimally in the field, regardless of the network conditions. This article delves into strategies, tools, and techniques that can significantly enhance user experiences in constrained environments.
The Imperative of Low Bandwidth Simulation
Why prioritize low bandwidth simulation? The answer is straightforward: millions of users in remote areas, along with rural and underserved regions, rely on mobile applications that can be suboptimal under duress. Understanding how these applications behave under low bandwidth conditions fosters a profound shift in perspective—it translates not just to technical efficacy but also accessibility and inclusivity for all users.
Understanding Bandwidth Constraints
Bandwidth, in its simplest form, refers to the maximum rate of data transfer across a network. Low bandwidth is typically characterized by limited data capacity and prolonged latency. It’s not merely a matter of speed; the quality of the connection can also fluctuate, leading to sporadic disruptions. Recognizing these nuances is crucial. For instance, a mobile application that requires constant connectivity might falter in performance or even become unresponsive, frustrating users immensely.
Techniques for Simulating Low Bandwidth
When it comes to preparing your app for low bandwidth environments, several methods can be employed to mimic these challenging conditions. Here are some key techniques to consider:
- Network Throttling: Modern development environments, especially those integrated with IDEs, often come equipped with tools that allow developers to throttle bandwidth. By mimicking various connection types—like 2G or reduced Wi-Fi speeds—developers can observe how their apps react under different conditions.
- Real Device Testing: While emulators and simulators provide a baseline understanding, nothing compares to testing on actual devices under real-world conditions. Deploying your app in areas where low bandwidth is prevalent will yield invaluable insights regarding performance and user interaction.
- Packet Loss Simulation: Low bandwidth scenarios are frequently accompanied by packet loss. By deliberately introducing packet loss in your testing environment, developers can identify how their application handles incomplete data transmissions and ultimately bolster its fault tolerance.
- Latency Adjustment: Bandwidth isn’t just about speed; latency plays a pivotal role as well. Adjusting the latency settings can help developers understand how their app performs with delayed responses—a common occurrence in low bandwidth situations.
Backend Optimization Techniques
Simulating low bandwidth is just part of the equation. To ensure that applications function proficiently, developers must also focus on optimizing the backend. Techniques to consider include:
- Data Streaming vs. Data Caching: Rethinking how data is transmitted can dramatically improve performance. Utilizing data caching allows applications to store frequently accessed data locally, reducing the need for constant server requests and effectively mitigating the impact of bandwidth limitations.
- Efficient Data Formats: Opt for lightweight data formats, such as JSON or Protocol Buffers, to minimize data size. Additionally, consider compressing images and other multimedia content. This reduction can make substantial differences in overall loading times and app responsiveness.
- APIs with Graceful Degradation: Building APIs that gracefully degrade functionality during poor connectivity is a critical aspect of developing resilient applications. While some features may become inaccessible, prioritizing core functionalities ensures that users can continue to derive value from the app.
User-Centric Design Considerations
The design and user experience of an app play a crucial role in its effectiveness in low bandwidth environments. Consider the following user-centric principles:
- Progress Indicators: Implementing loading animations or progress indicators reassures users that the app is responsive and actively working, even if loading times are extended during low bandwidth conditions.
- Simplified User Interfaces: A clean and minimalist design aids in quick navigation and reduces cognitive load on users, especially when they experience lag in loading components.
- Offline Functionality: Developing a robust offline mode allows users to access certain functionalities without a stable connection. This feature not only enhances user satisfaction but fundamentally broadens the app’s usability.
Continuous User Feedback and Iteration
Once an app has been deployed in low bandwidth areas, continuous user feedback is vital. Establishing channels for users to provide insights and report issues will empower developers to make iterative improvements. Real-world usage data can uncover unanticipated performance bottlenecks and guide future development strategies. Gathering feedback also enhances user trust, making them feel valued and heard.
Conclusion: Embracing Resilience in App Development
In an age where digital services are a fundamental necessity, simulating low bandwidth conditions is not just a technical exercise but a commitment to inclusivity. By understanding the challenges associated with low connectivity and employing strategic simulation techniques, developers can foster app resilience. Ultimately, this approach transforms your application into a versatile tool capable of serving diverse user needs, regardless of their circumstances. As you embark on this journey, remember: optimizing for low bandwidth not only protects your technical integrity but also elevates the user experience to unprecedented heights.