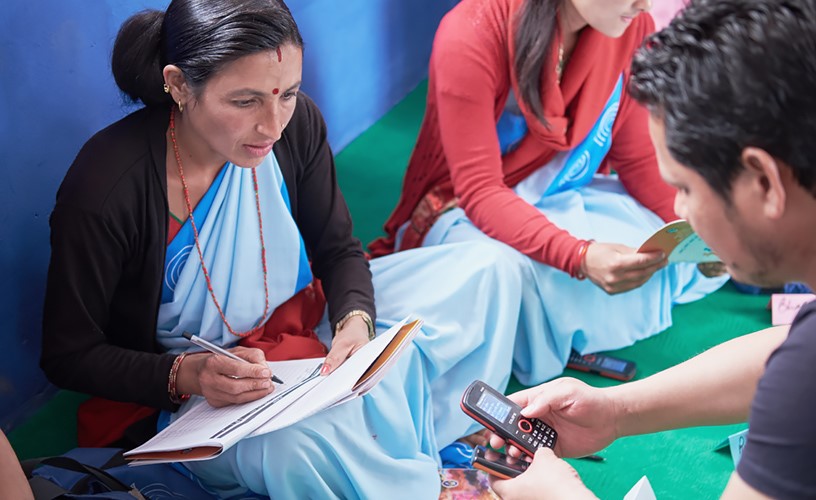
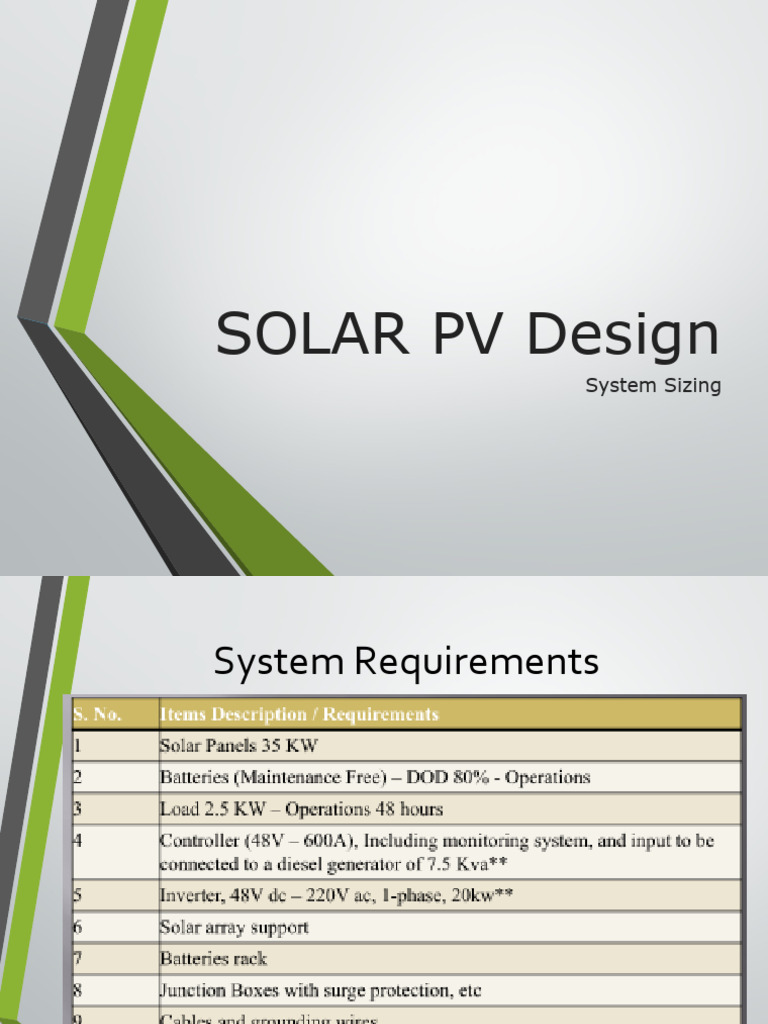
Last mile mobile solutions have emerged as a critical component in the landscape of aid distribution, transforming how humanitarian efforts allocate resources to those in dire need. This final segment—often riddled with logistical challenges—has traditionally been perceived as the Achilles’ heel of supply chains. However, with the advent of innovative mobile technologies, aid organizations are discovering new efficiencies that can enhance their operational frameworks. These cutting-edge solutions streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately ensure that assistance reaches its intended recipients swiftly and effectively.
At the heart of last mile mobile solutions lies the inherent flexibility they provide. Conventional methods for managing aid distribution often struggle with navigating unpredictable terrains, fluctuating demand, and communication barriers. Mobile applications and platforms allow on-the-ground workers to manage real-time data more effectively. With geolocation features, workers can swiftly identify those in need, alleviating the more burdensome aspects of logistical planning.
One of the critical benefits of last mile mobile solutions is their ability to provide up-to-the-minute information regarding inventory levels. Imagine a scenario where aid workers can utilize applications that communicate directly with suppliers in remote areas. These applications create a feedback loop where stock levels are instantly relayed back to distribution centers. Implementing such a system not only shaves hours—if not days—off routine operations but also deftly minimizes wastage. Aid organizations can distribute the right amount of goods in an optimized manner, thereby conserving precious resources.
Moreover, the implementation of mobile solutions facilitates streamlined communication among various stakeholders in the supply chain. For instance, with integrated messaging systems, various actors—from program managers to field staff—can share insights and updates in real-time. This communal knowledge fosters transparency, a crucial element in building trust among donors, recipients, and operational teams. When stakeholders are equipped with a common platform for sharing information, they are less likely to experience the disconnect that often stymies aid distribution efforts.
As we delve deeper, we uncover the crucial element of data analytics embedded within last mile mobile solutions. By employing sophisticated data collection mechanisms, organizations can analyze trends and patterns in aid distribution. How often is aid reaching its destination? Are certain demographics being underserved? The answer to these pressing inquiries lies within the comprehensive analytics these solutions offer. Employing data analytics not only augments decision-making processes but also enables organizations to tailor their interventions more closely to the specific needs of different communities, leading to more sustainable outcomes.
Security is another pivotal feature that enhances the reliability of mobile solutions. Addressing concerns around theft or misallocation, modern systems often incorporate verification mechanisms such as biometric authentication. These tools ensure that aid reaches the intended recipients, adding an extra layer of protection to incredibly vulnerable populations. Such technological safeguards dispel doubts and instill confidence, not only among those giving but also among those receiving aid.
Another striking advantage of last mile mobile solutions is the potential for increased community engagement. In conventional models of aid distribution, recipients often remain largely passive, receiving what is dispensed without an avenue to voice their needs or concerns. Mobile platforms can facilitate two-way communication, allowing beneficiaries to provide feedback on the types of aid received. This depth of interaction cultivates a sense of ownership and responsibility within communities, empowering them to take an active role in their welfare.
Furthermore, many last mile mobile solutions are designed with scalability in mind, making them adaptable to varied levels of need—from small, local initiatives to large-scale, international relief operations. For example, a small community affected by a natural disaster may require swift assistance, while a larger population facing chronic issues might need more extensive support over a prolonged period. Mobile solutions can be effortlessly adjusted to meet these divergent needs, ensuring that aid flows are not significantly disrupted. This adaptability is what makes these tools indispensable; they can pivot as situations evolve, maintaining their relevance and efficacy.
Despite the myriad benefits, the integration of last mile mobile solutions is not devoid of challenges. Organizations must invest in training and infrastructure to ensure that staff members are adequately prepared to utilize these systems. In regions with limited connectivity, the reliance on mobile technology could inadvertently exclude the most vulnerable populations unless creative solutions are implemented. Organizations may need to deploy offline functionalities, ensuring that aid workers can continue their efforts regardless of internet availability.
In conclusion, the fascination surrounding last mile mobile solutions stems from their undeniable impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of aid distribution. By embracing innovative technologies, organizations are not merely responding to the logistical challenges of the last mile; they are reshaping how humanitarian assistance is conceptualized and executed. The possibilities are expansive, suggesting that as more aid organizations become aware of these advancements, we may witness a substantial shift in the paradigm of global aid distribution. This evolution offers a beacon of hope in a world that desperately craves efficient, equitable, and empathetic responses to crises.